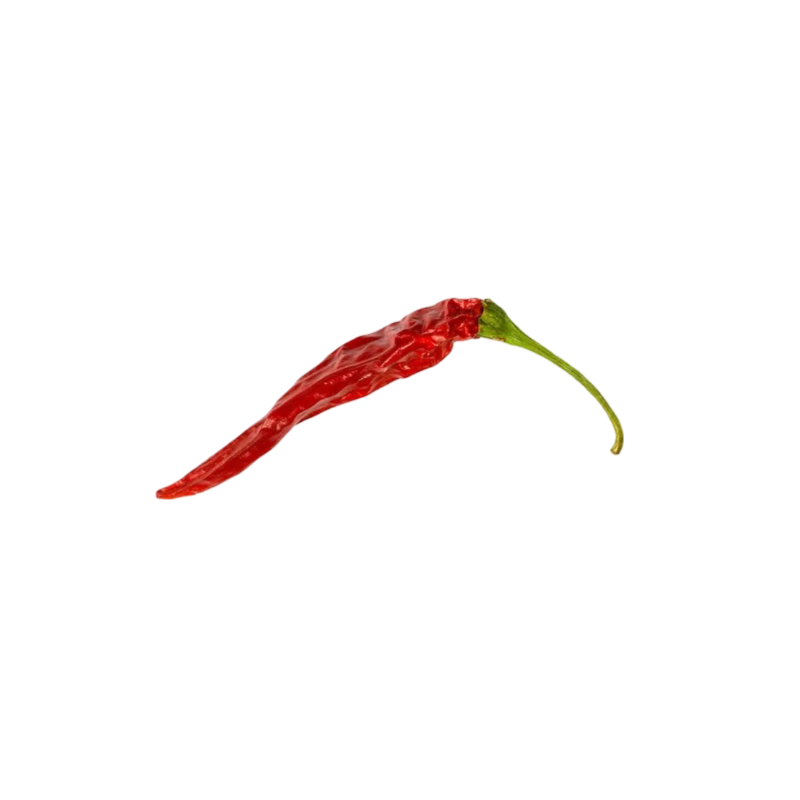
Cayenne pepper
Foodette, the home-delivered gourmet cooking basket, was one of our privileged partners. We developed a whole range of berlingots in their brand image. Following their closure, we are now offering the Foodette range of berlingots on clearance.
It's the same promise as our other berlingots: we grind and assemble the spices just before packaging, to give you a spice as if you'd just ground it. The only difference is the design.
Last but not least, you'll find some brand-new references, such as organic & IGP Kampot pepper, Cayenne pepper and Origan de Provence.
Foodette berlingots have a best-before date of 2026.
-
Net weight : 0,5g

History
Plant & perfume
The Cayenne pepper, originally from South America, is closely linked to the history of European colonization. This variety of chilli owes its name to the town of Cayenne, in French Guiana, although it was originally cultivated by the indigenous populations of Central and South America long before the arrival of Europeans.
The first Spanish and Portuguese explorers discovered these peppers on their travels in the 15th century and quickly introduced them to Europe. Christopher Columbus was one of the first Europeans to bring back these pungent fruits, presenting them as a revolutionary condiment different from traditional black pepper.
Over the centuries, Cayenne pepper spread around the world via trade routes. European merchants introduced it to Africa, Asia and especially India, where it became an essential ingredient in many local cuisines. Its popularity grew for both its culinary and medicinal qualities.
Today, the cayenne pepper is grown in many tropical and subtropical countries, representing a symbol of cultural and culinary exchange between continents.



Benefits
Cooking and Virtue

Origins
A long journey
Cayenne pepper, also known as red pepper or capsicum, has its roots in the tropical and subtropical regions of South America, mainly Brazil and Mexico. Archaeologists have discovered evidence of its cultivation by Amerindian populations dating back over 7,000 years.
Pre-Columbian civilizations, notably the Aztecs and Mayans, were already using chillies not only as a condiment, but also as a medicine and an important cultural element. They cultivated it in their gardens and incorporated it into their rituals and medicinal practices.
When Christopher Columbus discovered America in 1492, European explorers were the first to bring the plant back to Europe. The Portuguese and Spanish quickly realized its potential and began distributing it through their trade networks, introducing it to Africa, Asia and India.
The term “Cayenne” refers to the capital of French Guiana, but paradoxically, the variety is not native to this region. Rather, it's a name given by the European settlers who standardized and spread this variety of pepper around the world.
Scientifically classified as Capsicum annuum, Cayenne pepper belongs to the Solanaceae family, which also includes tomatoes and potatoes. Its worldwide popularity has been built on its distinctive taste and ability to adapt to different climates.


You might also like

6 other products in the same category:

Customers who bought this product also bought: